In this article, you will discover how a VoIP gateway transforms your telephone system by leveraging analog (FXS/FXO), ISDN (BRI/PRI) and SIP interfaces to efficiently connect your IP network. With clear technical explanations and a comparison with a traditional PBX, learn why adopting VoIP is essential to reducing your costs and simplifying your calls.
Points to remember
- A VoIP gateway translates the flows between traditional telephony and the IP network, enabling you to keep your existing equipment while switching to all-IP.
- It’s a modern way for companies to cut costs and simplify call management.
- Compared to a traditional PBX, the gateway offers greater flexibility and prepares the ground for cloud infrastructures. cloud infrastructures.
- Migration requires a method: assess the existing situation, choose the right solution, test and adjust.
- There are pitfalls (compatibility, network configuration, choice of model), but if properly anticipated, they won’t hinder the transition to high-performance IP telephony.
VoIP gateway definition and operation
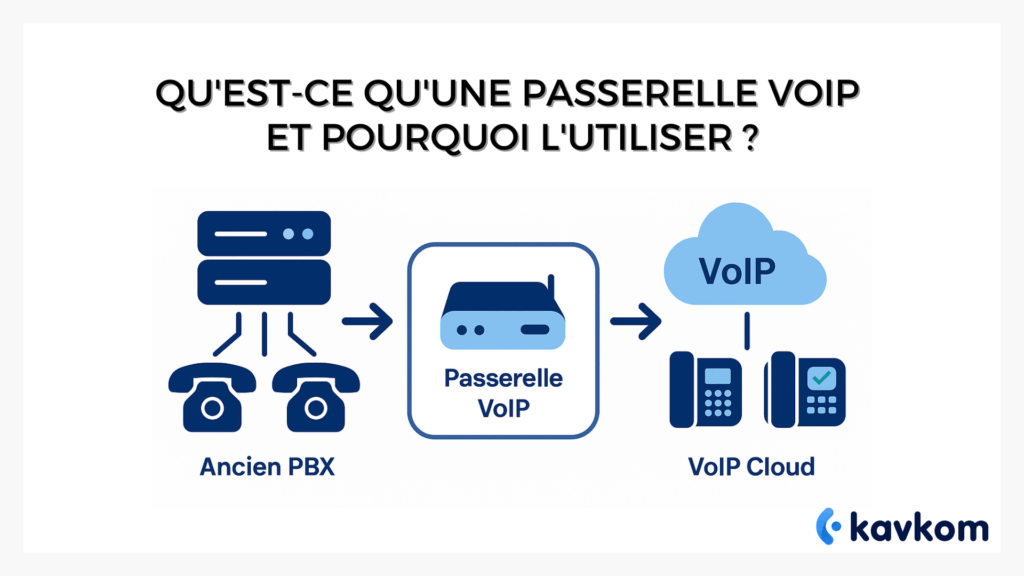
A VoIP gateway acts as a translator between two worlds. On the one hand, the traditional telephone lines still present in many companies. On the other IP telephonywhere voice travels in data packets over an IP network. The gateway is the network device that links the two worlds, enabling seamless communication.
What exactly is a VoIP gateway ? Imagine a box placed between your old switchboard and the Internet. It routes calls by transforming voice into digital signals (or vice versa, depending on the direction). The gateway can be analog (FXS/FXO), ISDN (BRI/PRI/E1/T1), GSM/4G or hybrid, depending on your needs, the type of lines used and the level of integration required.
The principle is simple: a gateway connected to the network breaks down the voice (a voice stream) into packets of data. These packets then travel via Voice over IP, before being reassembled so that the other party can hear a fluid conversation. This is known as full-duplex communication: the gateway ensures that every sentence, every word, travels in both directions without loss.
In a VoIP system, the gateway therefore plays a central role: it enables the use of existing telephones while opening the door to all-IP. It is this ability to operate directly on the network that makes it a key tool for companies in transition.
Express glossary – understanding VoIP gateways
- Voice over IP = voice transmission over the Internet.
- VoIP gateway = box connecting conventional lines to the IP network.
- SIP = standard protocol used for IP telephony.
- Bidirectional load = ability to send and receive voice at the same time.
The benefits of a VoIP gateway for optimized telephony
Arcep regularlyreminds us that the end of the copper network in France is prompting companies to modernize their infrastructures and switch to IP telephony. In other words, it’s no longer a question of if, but when, businesses should adopt modern VoIP. VoIP gateways thus become a key link in ensuring communications continuity and preparing for a smooth transition.
With a gateway, you can continue to receive calls on your existing lines while enjoying VoIP services and the benefits of a modern cloud-based solution. Installation is fast, compatibility extensive, and management simplified for your teams.
Why choose VoIP as the ideal solution?
- Lower costs: less cabling, maintenance and licensing.
- Flexibility: lines can be added or removed without reinstalling a complete system.
- Easy to install: the gateway acts as a bridge, compatible with your existing equipment.
- Centralization of voice calls: all flows are routed via the IP network, facilitating supervision.
- Opening up to unified communications: voice is at the heart, and CRM integration enables centralized customer data.
A gateway isn’t just a “technical box”. It’s a tool that transforms an old switchboard into an ideal solution, capable of handling today’s and tomorrow’s calls, while paving the way for a complete migration to a VoIP system.
VoIP gateway vs. traditional PBX
Traditional PBX; solid but closed
The PBX (or PABX) is theprivate branch exchange (PBX) that has long been the mainstay of the corporate world. Connected to the conventional telephone network(PSTN, ISDN), it relies on physical lines and conventional telephones.
Its limitations are clear:
- Heavy installation, with lots of wiring and maintenance.
- High fixed costs (equipment, contracts, technicians).
- Low scalability: every new line becomes a project.
- Virtually no integration with modern digital tools.
VoIP gateway: the agile compromise
The VoIP gateway acts as a translator between existing analog telephones and IP telephony. Specifically, it connects to the IP network and analogtelephone lines via FXO/FXS ports (often 4 or 8). Itroutes voice calls and supports two-way communication between old equipment and new VoIP services.
In its guides on system interconnection, the ANSSI reminds us that a gateway is a network device used to partition and secure data flows. In the case of VoIP, it plays the same role: ensuring compatibility while providing a secure technical framework for your communications.
Kavkom: going 100% cloud
With Kavkom, there’s no need to compromise. Instead of piling up hardware and updates, everything is moved to the cloud:
- Immediate commissioning, no physical gateway required.
- Responsive human support to guide you.
- Pro rata billing, no obligation.
It’s the difference between tinkering with an old system to adapt it, and going straight to work on a modern solution designed to evolve.
Technical and economic criteria
Analog logic
Older installations are based on analog gateways and PSTN-compatible equipment. Each line requires physical ports: FXO, FXS, sometimes in 4-port or 8-port versions. These solutions make it possible to connect analog telephone lines or fax machines, but require dedicated hardware and ongoing maintenance. Each capacity extension means new purchases and new configurations.
The hidden costs of traditional
A conventional telephone system quickly accumulates :
- Purchase of analog equipment.
- Licenses for each port or extension (e.g. 4 FXS ports).
- Software updates and support.
- Dependence on a PSTN or ISDN operator.
It’s a stable but rigid infrastructure, where every evolution has a financial and logistical cost.
The all-IP economy
With IP telephony, the same functions are available via a simple Internet connection. No need to switch via FXO or FXS ports : voice travels directly over the VoIP network. Updates are centralized in the cloud, and lines are created in just a few clicks, without technicians or delays.
Kavkom, the simple scale
Where a gateway or PBX requires constant hardware monitoring, Kavkom offers a 100% software-based alternative. No ports to manage, no boxes to maintain: features are delivered ready to use. Human support takes care of initial configuration, and pro rata billing eliminates the fixed costs associated with extensions.
In a nutshell:
- Analog = hardware, cabling, licenses.
- IP = flexibility, scalability, variable costs.
- Kavkom = a modern, hardware-free solution designed for everyday call center use.
Guide to migrating to a hardware-free VoIP infrastructure
Step 1: Assess your current system
Before any migration, you need to know where you’re starting from. List your telephone lines and identify whether you’re still using analog lines connected to an old PSTN switchboard. Also check the condition of your internal telephone network: cabling, handsets, compatibility.
The aim is simple: to identify the points that are holding us back and those that can be maintained.
Practical tip: draw up a clear map of your existing telephone equipment, to avoid any surprises during the switchover.
Step 2: Choosing the right solution
Once the inventory is complete, it’s time to select a modern solution. Several options are available: IP gateways to connect your current equipment to the all-IP network, or a complete switchover to a cloud platform. Manufacturers such as Yeastar and Grandstream offer intermediate equipment, but these still require technical management.
Conversely, relying directly on a service provider like Kavkom simplifies the migration process. The solution is compatible with your current uses, but without requiring you to maintain physical hardware.
Step 3: Implement and test the solution
It’s time to take action. The idea is not to cut everything overnight, but to migrate gradually. A pilot can be set up on a small team before migrating to the whole center.
Configuration is cloud-based: all you need is an Internet connection, supported by a stable Ethernet cable. Modern telephony systems are based on ToIP (Telephony over IP), making it easy to connect your existing center systems.
With Kavkom, installation is immediate: no hardware to plug in, just online activation. You can test calls in-house, measure quality and adjust routing rules without tying up your teams.
Step 4: Monitoring and optimization
A successful migration doesn’t stop at “go live”. You need to track performance: pick-up rates, waiting times, customer satisfaction. A modern solution like Kavkom offers real-time dashboards, where every interaction is visible and can be analyzed.
Messaging integration, multi-channel management and unified communications then take care of the whole company’s communications, far beyond just voice.
Pitfalls to avoid when installing a VoIP gateway
Installing a VoIP gateway isn’t rocket science, but some mistakes can be costly. The first pitfall is choosing a model that is incompatible with your current infrastructure. For example, a GSM VoIP gateway won’t be useful if you have no need to connect mobile lines to the fixed line. Conversely, ignoring BRI/ISDN constraints can block your extensions or prevent certain switches from working properly.
Another common pitfall is forgetting to check compatibility with your analog phones. Some configurations require specific ports (FXS/FXO), without which it’s impossible to route calls to the right extension.
Finally, many people underestimate network configuration. The gateway must be correctly connected to the IP network and tested under real-life conditions. Incorrectly dimensioned gateways create bottlenecks, interruptions or loss of voice quality.
Practical advice to avoid unpleasant surprises
- Check your real needs (mobile lines, VoIP to fixed, etc.) before you buy.
- Check compatibility with your existing hardware (analog, PBX, handsets).
- Test the gateway in a pilot environment before global deployment.
- Secure network configuration (QoS, dedicated bandwidth).
FAQ – Frequently asked questions
What is a VoIP gateway?
A VoIP gateway is a piece of equipment that converts the flows of a conventional telephone system into VoIP. In concrete terms, it’s the answer to the question “What is a VoIP gateway? a box that links IP and traditional telephony.
How does a VoIP gateway work, and what impact does it have on telephony?
The gateway acts as a translator. It transforms voice into data packets over the IP network. This VoIP system, based on Voice over IP and IP telephony, can be linked to a SIP account to manage internal and external calls.
What’s the difference between a VoIP gateway and a GSM VoIP gateway?
The difference lies in the type of link. A GSM VoIP Gateway connects VoIP to GSM mobile networks, making it ideal for routing voice calls to or from mobiles. VoIP services, on the other hand, are limited to the Internet.
Conclusion
The VoIP gateway remains a strategic building block for linking the old PSTN world to the all-IP world. Companies choosing modern VoIP gateways are taking a step towards IP telephony and a more flexible VoIP network.
For some, the gateway is the simplest modern solution; for others, a direct switch to the cloud represents the ideal solution. Either way, these technologies pave the way for more efficient unified communications.
It’s up to you to find the formula that suits your infrastructure and your objectives.