This comprehensive guide provides you with a clear, step-by-step method for clearing up any doubts you may have about the differences between ToIP and VoIP. You’ll find a precise comparison table, a step-by-step procedure for choosing the ideal telephony system, and answers to essential technical questions about IP protocols. You’re well on the way to finding the right solution for your infrastructure, and getting your business communications under control.
Points to remember :
- IP telephony transforms voice into data, providing a flexible basis for modernizing business communications.
- The distinction between VoIP and ToIP is based on their role: VoIP carries voice, ToIP organizes the entire telephony system.
- Technical differences mainly concern protocols, architecture and quality of service, which depend directly on the local IP network.
- The benefits and limitations of each solution vary: VoIP reduces costs and simplifies calls, while ToIP provides complete, scalable management.
- Follow our step-by-step guide (requirements, integration, costs) to choose the most suitable solution and make your transition to the cloud a success.
Understanding the fundamentals of IP telephony
With IP telephony, your calls travel over the IP network in exactly the same way as other digital traffic. Your photos, videos or e-mails already travel in packets; voice over IP follows the same path. You speak, the voice is transformed into small digital chunks, sent and then reconstituted at the other end.
In France, this move is part of the transition from the historical telephone network (PSTN) to all-IP. In its reference document, Orange describes the main stages in this process – the cessation of production of PSTN lines, gradual switchover by zone, IP-based substitution solutions – and explains how it will be achieved. The evolution of fixed telephony towards all-IP.
Defining VoIP and ToIP
VoIP(Voice over Internet Protocol) describes the way voice travels over an IP network. Your speech is transformed into digital data, sent in packets and then reassembled on arrival. With this technology, you make a call as usual, but instead of using a traditional telephone line, the conversation is carried over the Internet.
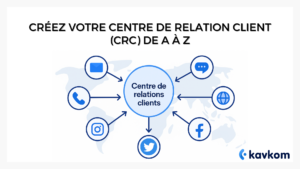
ToIP(Telephony over IP) goes even further. It encompasses the entire IP telephony service within a company: dialing, intelligent call routing, queuing, interactive voice server, real-time supervision and integration with your business tools. In other words, VoIP is the voice transport medium, while ToIP organizes and enriches the day-to-day telephony experience.
- VoIP: transport technology (voice becomes IP packets).
- ToIP: business telephony service based on VoIP(call management, supervision, integration).
Technical differences between VoIP and ToIP
VoIP relies on standard protocols such as SIP to establish calls and RTP to transport audio. ToIP integrates these building blocks, but adds an organizational layer that manages the business logic: which calls have priority, who should answer, how to monitor quality. In other words, VoIP provides the basic mechanics, ToIP orchestrates everything else.
Comparison of architectures and protocols
VoIP can be operated using a simple software application (softphone) or an IP phone connected to the network. It requires a stable connection and sufficient bandwidth, but remains fairly lightweight. ToIP, on the other hand, mobilizes a more structured telephony system: an IPBX (virtual or physical), an interactive voice server, CRM integrations, or even several interconnected sites.
In terms of protocols, VoIP is based on a number of well-established standards:
- SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) to manage the opening, modification and closing of sessions.
- RTP (Real-Time Transport Protocol) for audio.
- Codecs such as G.711 or G.729 for voice compression and transmission.
ToIP takes these elements, but combines them with other layers: management of routing rules, dashboards, secure storage of recordings. This is where the role of theoperator or solution provider is decisive: it provides not only connectivity, but also the platform for managing the entire communications cycle.
Service quality and safety
Call quality depends above all on the network. VoIP reacts badly to long delays (latency), variations in tempo (jitter) or packet loss. To avoid these effects, QoS(Quality of Service) is implemented on the local IP network. In concrete terms, this means giving voice traffic priority over other uses, such as web browsing or downloads. Properly set up, this priority ensures stable sound, comparable or even superior to that of traditional telephone lines.
The question of security is just as central. An IP infrastructure can be exposed to eavesdropping, saturation attacks or intrusions. ANSSI reminds us that telephony must be protected like any other digital service. In its guide to IP telephony, the agency recommends flow encryption (SRTP, TLS), network separation and active monitoring.
ToIP adds an organizational layer to this protection. Call recording, live supervision or integration with a CRM system require precise rules: access management, traceability and regular backups. So a telephony system is not just a technical infrastructure; it’s also a framework that ensures the confidentiality and reliability of all your telephone communications.
Advantages and disadvantages of VoIP and ToIP solutions
Choosing between VoIP and ToIP isn’t just a matter of comparing two technical acronyms. It’s about thinking about how your company wants to manage its telephony system in the future: simple voice transport, or complete call and organization management. The differences between the two lie in costs, flexibility, security and integration with your business tools.
VoIP: benefits and limitations
The first obvious advantage of VoIP is lower costs. Calls are routed via the Internet rather than a traditional network, which means lower communication costs, particularly for international calls. It also brings flexibility: you can call from a computer, smartphone or IP phone, as long as the connection is stable.
Voice over IP is also easy to upgrade: you can add new lines without any major work or complex equipment. It’s an attractive solution for SMEs that want to centralize communications without embarking on a complete organizational overhaul.
But VoIP has its limits. Its quality depends directly on the network. Too much latency, jitter or packet loss, and conversation becomes tedious. Security must also be reinforced: without encryption, flows can be intercepted. Finally, VoIP alone does not provide advanced functionalities (supervision, queuing, intelligent routing). It carries the voice, but does not structure all your uses.
ToIP: benefits and limitations
ToIP takes VoIP and adds an organizational layer. It transforms voice transport into a complete telephony system, designed for the enterprise. The benefits are numerous:
- Better flow management thanks to queues, interactive voice server and routing rules.
- Seamless integration with your business tools (CRM, ERP).
- Real-time supervision to monitor indicators and coach your teams.
- Easier scalability: you open a new site, add agents, everything goes through the platform.
ToIP, on the other hand, requires more parameterization and special attention to the local IP network. If your infrastructure isn’t prepared (bandwidth, QoS, segmentation), the experience can quickly deteriorate. It can also represent a higher initial investment, even if this is offset by the productivity and enhanced quality of telephone communications.
Step-by-step guide to choosing the right solution
Here’s a simple three-step method for getting ahead without getting bogged down in details.
Step 1: Identify your telephony needs
Start by observing your reality. How manycalls does your team handle every day? Are they mainly inbound (customer service) or outbound (prospecting)calls? Do you need to record certain conversations, manage queues, or give managers a hand in monitoring live performance?
This snapshot of your usage determines the type of telephony you need. A small structure with a few workstations may be satisfied with a simple VoIP service. A customer relations center with dozens of agents, on the other hand, will have to rely on ToIP telephony, capable of managing both volume and supervision.
Tip: make a list of the features you’re missing today. This is the best way to clarify your priorities and guide your choice of future telephony system.
Step 2: Assess integration with existing systems
A telephony project never arrives in a vacuum. It fits into an environment where customer data, a local IP network with its constraints, and business tools (CRM, ERP, helpdesk) are already in circulation. So the right question to ask is: “How will the solution interact with the rest?”
A suitable platform must speak the right protocols (SIP for signaling, RTP for audio), but also offer native integrations with your tools. A sales rep doesn’t have to enter a prospect’s details twice: the record should open automatically as soon as the call is taken.
This is where cloud solutions like Kavkom stand out. The platform integrates with the major CRMs (Zoho, Salesforce, HubSpot…) and works just as well with a softphone as with a physical IP phone. This compatibility reduces friction and speeds deployment.
Step 3: Analyze costs and flexibility
Beyond the technical aspects, the budgetary question is crucial. How much does the service really cost, and above all, how much flexibility does it offer? Some operators impose rigid subscriptions with multi-year commitments. Others offer prorated billing: you only pay for what you use, and you can suspend lines when activity drops.
Here again, the difference is clear. With a cloud telephony system, users can be added or removed in just a few clicks, with no hidden costs or delays. For an SME, this flexibility is a guarantee of cost control. For a call center, it’s a way of adjusting capacity according to ongoing campaigns.
Kavkom is a good example of this model: no commitment, pro rata billing, unlimited calls depending on the package chosen, and real-time supervision. These choices reflect a simple philosophy: adapt telephony to your rhythm, not the other way around.
We retain :
- Take stock of your needs (volume, type ofcalls, supervision).
- Check compatibility with your local IP network and business tools.
- Compare costs and flexibility, preferring offers with no commitment and no hidden charges.
Recommendations for a successful transition to new telephony
Migrating to IP telephony should not be seen as a break with the past, but rather as a gradual evolution. With the right preparation, the transition not only improves communications quality, but also team productivity. Here are three simple levers to support this transition.
First, monitor your calls right from the start.
Real-time supervision enables you to spot a sound problem, a long delay in a queue, or an agent in need of help, immediately. It’s a way of continuously adjusting configuration and reassuring your teams.
Then, pay particular attention to integration with your business tools.
Linking your IP telephony solution to a CRM avoids duplicate data entry and streamlines customer relations. An incoming call can automatically trigger the opening of a customer file; an outgoing call can be effortlessly logged. This kind of automation, made possible by the right protocols (SIP, open APIs), lightens the administrative load and refocuses your staff on added value.
Last but not least, rely on technical support.
A successful transition also depends on the responsiveness of your contacts. Make sure that your supplier is easy to reach, offers human support and helps you configure your routing rules and integrations. This follow-up ensures that your migration is not a static project, but one of continuous improvement.
Keep in mind:
- Supervise your calls right from the start to stay in control.
- Integrate telephony with your business tools to streamline communications.
- Choose a partner who offers real support, not just a platform.
FAQ – Frequently asked questions
What’s the difference between ToIP and VoIP?
The differences between the two lie in their scope. VoIP and ToIP use the same protocols to transport voice, but VoIP is limited to transport. ToIP adds the whole business organization: dialing, queuing, supervision.
What is ToIP telephony and how does it work?
ToIP is a complete IP telephony service. It is based on a local IP network and standard protocols. Voice is transported as data packets (VoIP), then enhanced with features such as intelligent routing, IVR or CRM integration.
How do I choose between VoIP and ToIP for my telephony system?
If you’re just looking to reduce youroperator costs, VoIP may be all you need. If your company needs a structured telephony system (supervision, CRM integration, routing), ToIP is more relevant. It all depends on your needs and the size of your team.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of VoIP compared with ToIP?
VoIP is simple and economical, but limited to voice transmission. ToIP is more complete and flexible, but requires a solid network and appropriate configuration. The differences between the two will guide your choice, depending on your performance and organizational needs.
Conclusion
IP telephony is certainly a technical evolution. But it’s also, and above all, a new way of thinking about your communications.
VoIP and ToIP each have their own advantages: one transports voice more economically, the other builds a telephony system that supports your business uses. Properly prepared, the transition to the cloud offers more agile, more integrated telephony, capable of supporting your growth projects.